Some disinformation groups go for low volume, high impact. Others go for the opposite.
The latter is the case with Russian-linked operators who, in late 2019, infamously leaked documents on trade discussions between the U.S. and the UK, according to a new report from researchers at Graphika.
The sheer scale of their work, which often had little uptake online, is what they say makes the so-called Secondary Infektion campaign unprecedented. So sprawling is the operation, Graphika has created a website to host the myriad disinformation ops of the group for the benefit of further research.
For six years, the disinformation specialists have been spreading fake stories and forged documents across all manner of social media and Web forums, all with the aim of sowing distrust and swaying elections across European and North American nations.
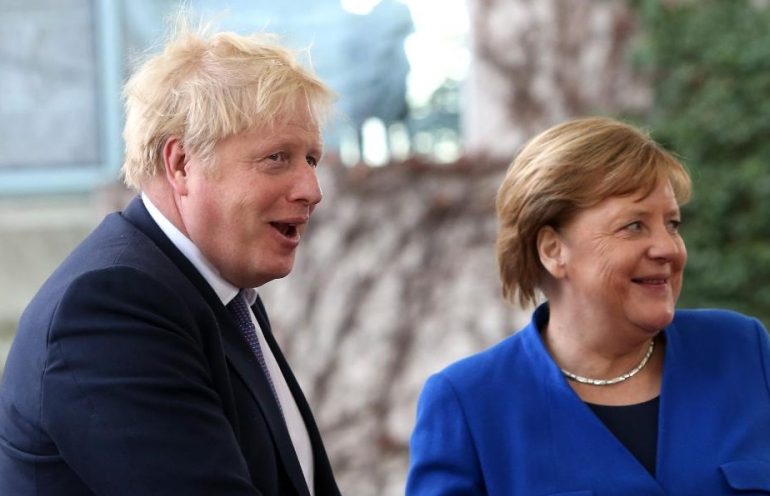
Inside one of Secondary Infektion’s more startling articles were claims that extremist Remainers were plotting to assassinate UK Prime Minister Boris Johnson and that German Chancellor Angela Merkel was an alcoholic. Then there were the more predictable attempts to sway elections, with incessant attacks on Hillary Clinton’s election campaign in 2016, some posts labeling her a “murderer,” followed by more of the same with Emmanuel Macron’s bid for the French presidency.
But, though their prolific output was unprecedented, they rarely went viral, according to the researchers, who say enduring mysteries surround the group. “Judging by the content they posted, it looks like the purpose was to undermine relations between countries that the operation saw as adversaries, to support Russian information operations against targets such as the World Anti-Doping Agency and the Ukrainian government, and to undermine Kremlin critics,” says Camille Francois, chief innovation officer at Graphika.
“But as long as the identity of the operators remains a mystery, there will be a question mark over what they were truly trying to achieve in the first place.”
How Secondary Infektion spread
Facebook first attributed the Secondary Infektion operation to Russian actors in May 2019. Then, in December 2019, Reddit attributed the leak of U.S.-UK trade leaks, which turned out to be genuine, to the same campaign. That was, in fact, the only real big-impact effort by the group as it sought to disrupt the UK election.
From there, Graphika was able to trace the operation back to its roots in 2016. From small, specialist Web forums to the sprawling platforms of Facebook, Twitter, YouTube, Medium, and Reddit, Secondary Infektion had extraordinary breadth. Its most common theme was to paint Ukraine as a failed state or untrustworthy partner, but it also tried to convince the world that the U.S. and NATO were aggressive and interventionist, the researchers said.
Europe was a target, too, often depicted in content as fractured and weak. Common themes ranged from Scottish and Catalan independence to older grievances such as the Armenian genocide.
Many posts contained negative content about immigration, often targeting Muslim refugees, linking them to terrorism and sexual violence. “The intent appears to have been to stir up racial and religious conflict in the target countries,” Graphika’s researchers wrote.
Various accounts set up by Secondary Infektion impersonated high-profile politicians, including U.S. Secretary of State Mike Pompeo, former White House chief of staff General John Kelly, and Sen. Marco Rubio (R-Fla.). One tweet from a counterfeit Rubio, for instance, accused the UK of interfering in the U.S.midterm elections of November 2018.
And in recent months, there were some efforts to point the finger at the U.S. for creating Covid-19, a much-maligned conspiracy theory. The name “Secondary Infektion” was given to the campaign in memory of the Soviet-era “Operation Infektion” that accused the U.S. of creating AIDS.
No desire for virality
Other than the trade leaks, none of these efforts went viral. Indeed, few of the campaign’s efforts over six years have made a major splash.
“Almost none of the operation’s posts across six years of activity achieved any measurable engagement, in terms of shares, likes, and positive reactions across platforms,” Graphika wrote. “This may indicate that the operators were not interested in engagement metrics – for example, if they were driven by production quotas rather than engagement targets – or that they were using some other form of metrics not visible to outside observers.”
Secondary Infektion hasn’t yet been seen in action around the 2020 U.S. election. But the expectation is that Russian disinformation and cyber espionage units will be back in earnest trying to sow more chaos in a country already besieged by Covid-19 and racial tensions.
"Forbes Georgia-ის სარედაქციო ბლოგპოსტების სერია "როგორ გამდიდრდა“ და "საქართველო რეიტინგებში".